Is physical activity delivered via the internet (!) effective in treating mild to moderate depression? We jsut did a trial and the results was just published in an open access paper entitled: “Internet-delivered therapist-guided physical activity for mild to moderate depression: a randomized controlled trial“.
Objective
The main hypothesis, and the objective of the study, was to test if the participants allocated to the treatment group would show a larger reduction in depressive symptoms than those in the control group.
Methods
This study was a randomized nine week trial of an Internet-administered treatment based on guided physical exercise for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). A total of 48 participants with mild to moderate depression, diagnosed using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders, were randomized either to a treatment intervention or to a waiting-list control group. The main outcome measure for depression was the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II), and physical activity level was measured using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). The treatment program consisted of nine text modules, and included therapist guidance on a weekly basis.
Results
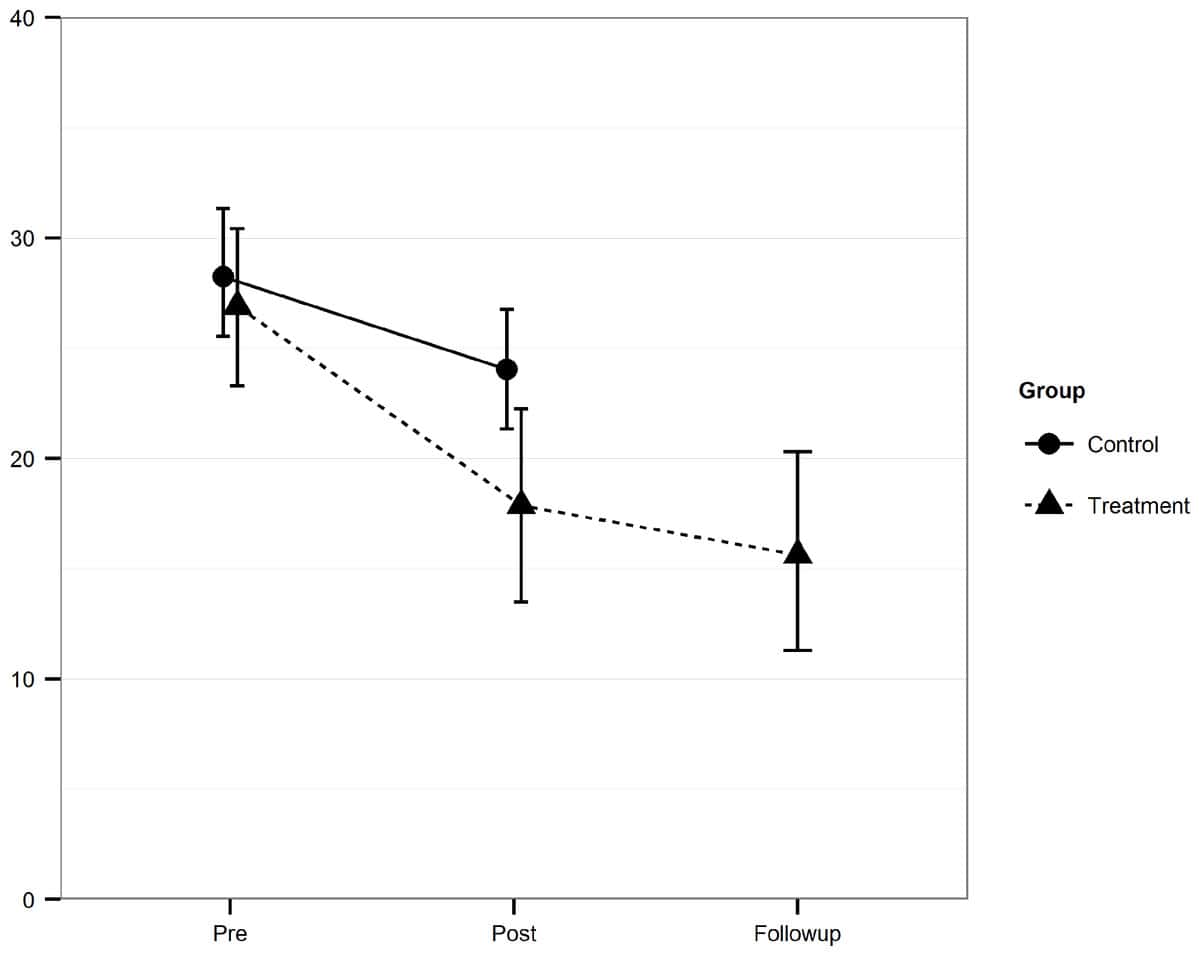
The results showed significant reductions of depressive symptoms in the treatment group compared to the control group, with a moderate between-group effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.67; 95% confidence interval: 0.09–1.25). No difference was found between the groups with regards to increase of physical activity level. For the treatment group, the reduction in depressive symptoms persisted at six months follow-up.
Conclusions
Physical activity as a treatment for depression can be delivered in the form of guided Internet-based self-help.
Referece:
Ström, M., Uckelstam, C.-J., Andersson, G., Hassmén, P., Umefjord, G., & Carlbring, P. (2013). Internet-delivered therapist-guided physical activity for mild to moderate depression: A randomized controlled trial. PeerJ, 1, e178.
The second generation of the treatment program is now being tested in a RCT named Actua!
[youtube]http://youtu.be/py9cwsNYj9w[/youtube]